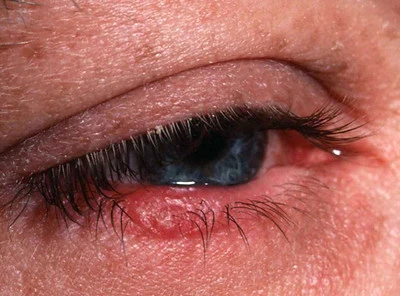
Diesel Exhaust Fluid, commonly used in modern diesel engines, harbors hidden risks for eye safety. Composed of 32.5% urea and 67.5% deionized water, DEF can cause significant irritation upon contact. This article explores the adverse reactions triggered when this fluid meets the delicate tissues of the eyes, leading to symptoms that range from mild discomfort to potential long-term damage.
Urea, a key ingredient in DEF, is responsible for irritation, redness, and a burning sensation. It disrupts the natural balance in eye cells, drawing out moisture and leading to dryness. Additionally, its pH level, higher than that of natural tear fluid, intensifies this irritation.
Short-term exposure can result in tearing and temporary blurriness, while prolonged contact poses risks like corneal damage and chronic dry eye. We will discuss the importance of proper handling, immediate response to exposure, and the necessity of protective eyewear. Understanding the risks of DEF is crucial for protecting your vision, emphasizing that caution is paramount in handling such substances.
Read on…
Understanding DEF Fluid
When dealing with Diesel Exhaust Fluid, it’s crucial to grasp its chemical composition and functionality, especially considering its potential hazards, including eye exposure. Here, I’ll guide you through the essentials of DEF fluid, focusing on its chemical makeup, how it helps in reducing vehicle emissions, and common scenarios where you might be exposed to it.
1. Chemical Composition of DEF
DEF fluid is a carefully balanced solution, primarily consisting of 32.5% urea and 67.5% deionized water. Urea, a compound formed from nitrogen and hydrogen (NH2)2CO, is key in the chemical reactions that reduce harmful emissions. This specific concentration, 32.5%, is critical – it’s the most effective ratio for converting NOx emissions into harmless nitrogen and water vapor in the Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) system of diesel engines.
2. How DEF Works in Reducing Vehicle Emissions
In the SCR system, DEF fluid is injected into the exhaust stream of a diesel engine. Here’s where the magic happens: when it vaporizes, it forms ammonia and carbon dioxide. This ammonia then reacts with the NOx emissions (a mix of nitrogen monoxide and nitrogen dioxide) in the presence of a catalyst. This reaction converts the NOx into nitrogen and water vapor – two harmless components that are naturally present in the atmosphere. The precision of this process is remarkable: it can reduce NOx emissions by up to 90%.
3. Common Situations for DEF Fluid Exposure
You’re most likely to encounter DEF fluid in a few key scenarios:
- Refilling Tanks: If you’re working with diesel-engine vehicles, especially heavy-duty trucks, you’ll often need to refill the tank.
- Handling Containers: Whether in transportation or storage, handling large containers or drums of fluid can lead to accidental spills.
- Maintenance and Repair: Mechanics working on SCR systems might come into contact with DEF residue.
- Accidental Spills: In industrial or automotive settings, it can spill during handling, leading to potential exposure.
Remember, while the fluid is not highly toxic, it can be irritating, especially to sensitive areas like the eyes. It’s crucial to handle it with care, using appropriate protective equipment, and to be aware of first aid measures in case of accidental exposure.
Read related article: How Do You Dispose of Old or Unused DEF?
The Science Behind DEF Fluid Eye Exposure
When it comes to understanding the impact of Diesel Exhaust Fluid on your eyes, it’s essential to delve into the chemical interactions and the potential effects, both short and long-term. I’ll guide you through this, using technical terms and relevant data, to provide a clear picture of what happens when it comes into contact with tissue.
Chemical Interaction Between DEF and Eye Tissue
DEF can have a significant impact on your eyes. The urea component, when it contacts this organ, can cause an osmotic imbalance. This means that the concentration of urea can draw out moisture from the tissues, leading to irritation. Additionally, the pH level, which typically ranges around 9-10, can further exacerbate this irritation because it’s higher than the natural pH of the tear film (around 7.4).
Short-term vs. Long-term Effects on the Eyes
- Short-term Effects:
- Redness and Irritation: Almost immediately upon contact, you might experience redness and a burning sensation.
- Tearing and Discomfort: Your eyes will likely produce excess tears in an attempt to dilute and flush out the DEF.
- Temporary Vision Blurriness: This is often due to tearing and potential corneal irritation.
- Long-term Effects:
- Corneal Damage: Repeated or prolonged exposure can lead to more severe issues like corneal ulceration.
- Chronic Dry Eye: Continued osmotic stress on the tissues can lead to chronic dry eye syndrome.
- Potential Vision Impairment: In severe cases, sustained damage to the cornea and other parts of the eye could lead to long-term vision problems.
Case Studies or Real Incidents
While specific case studies or incidents involving DEF exposure are not commonly detailed in public records, occupational health reports have noted instances where workers in automotive industries have experienced injuries due to accidental splashes. These cases emphasize the need for proper safety equipment, like goggles, and prompt washing with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes following exposure.
Remember, the key to handling DEF safely is understanding the risks and taking proactive measures to protect yourself. In case of exposure, immediate and thorough rinsing and seeking medical attention are crucial steps. Stay informed and always prioritize safety in handling such substances.
Read related article: Is Def Fluid Harmful To Skin? (Its pH Factor)
First Aid and Immediate Response for DEF Eye Exposure
If you’ve just experienced exposure to your eyes, acting quickly and efficiently is crucial. DEF can cause significant irritation and damage. Here’s a step-by-step guide on what to do immediately following exposure:
Step-by-Step Immediate Response
- Immediate Rinsing: As soon as it contacts, head straight to a water source. Flush your eyes with clean, lukewarm water for at least 15 to 20 minutes. Keep your eyelids open and roll your eyes around to ensure water reaches all parts of the eye.
- Remove Contact Lenses: If you wear them, remove contact lenses immediately, but only after starting the rinsing process. Don’t waste time removing them before rinsing, as every second counts in reducing damage.
- Continue Rinsing: Even if you feel relief, continue rinsing for the recommended duration. This prolonged flushing helps dilute and remove the DEF from your eye tissues.
- Seek Medical Attention: After rinsing, seek medical attention, even if your symptoms seem to subside. Chemical exposure can have delayed effects, and a healthcare professional can assess for any potential damage.
Importance of Prompt Medical Attention
- Assessment of Damage: A healthcare professional can determine the extent of the eye damage, which might not be immediately apparent.
- Prevention of Long-term Effects: Prompt medical intervention can help prevent long-term complications like corneal damage or chronic dry eye.
- Professional Cleaning: Doctors can perform a thorough cleaning and provide appropriate treatments, such as eye drops or medications, to mitigate the effects of the exposure.
Why Common First Aid Measures Might Not Be Adequate
- Insufficient Rinsing Time: Standard first aid might suggest a shorter rinsing time, but fluid exposure requires at least 15 to 20 minutes due to its chemical properties.
- Delayed Symptoms: Some symptoms of damage from DEF might not appear immediately. Without a thorough medical examination, these delayed effects could lead to long-term damage.
- Its Chemical Properties: The specific concentration of urea can lead to unique osmotic and pH imbalances in the eye, requiring more specialized treatment than standard irritants.
Remember, your eyes are delicate and vital organs. Taking immediate and appropriate action following exposure is key to minimizing harm and protecting your vision. Always err on the side of caution and seek professional medical advice promptly.
Read related article: Is Def Fluid Flammable? (Its Flash Point & Auto Ignition)
Medical Perspective: Understanding the Risks and Treatment of Exposure
If you’ve ever been concerned about the risks associated with Diesel Exhaust Fluid coming into contact with your eyes, you’re right to be cautious. Based on insights from ophthalmologists and toxicologists, let’s delve into the medical risks and treatments associated with exposure to the eyes, as well as the long-term prognosis.
Interview Insights: Ophthalmologist/Toxicologist on DEF Fluid Eye Risks and Treatment
- Chemical Burn Risk: An ophthalmologist would categorize it as a mild to moderate alkali burn due to the higher pH level compared to natural tears.
- Immediate Treatment: The first step is thorough irrigation. You should rinse your eyes with lukewarm water or a saline solution for at least 15-20 minutes. This dilutes and washes away the fluid, reducing the severity of the burn.
- Medical Evaluation: Following immediate rinsing, it’s crucial to visit a specialist. They can assess the extent of the damage using a slit lamp examination and may apply a fluorescein dye to highlight any corneal abrasions.
- Treatment Protocol: Depending on the severity, treatment might include antibiotic eye drops to prevent infection, steroid eye drops to reduce inflammation, and lubricating eye drops to alleviate dryness.
Long-term Prognosis
- Minor Exposure: For minor exposures with immediate and appropriate treatment, the prognosis is generally good. Most individuals recover without any long-term effects.
- Repeated or Severe Exposure: This can lead to chronic issues like corneal ulceration or scarring, which might impair vision. In severe cases, surgical interventions like corneal transplants might be necessary.
- Prevention Is Key: Consistently wearing safety goggles when handling it and following safety protocols can significantly reduce the risk of exposure.
Remember, while DEF is not corrosively toxic, its chemical properties can cause significant irritation and damage. Taking immediate action following exposure and seeking professional medical advice is crucial. As with many chemicals, the long-term prognosis is much more favorable when you act quickly and responsibly at the first sign of exposure.
Preventative Measures: Safeguarding Yourself from DEF Fluid Exposure
When dealing with Diesel Exhaust Fluid, safety should always be your top priority. Whether you’re in an occupational setting or handling it at home, there are specific protocols and personal protective equipment (PPE) you should use to avoid exposure. Here are some key preventative measures to keep in mind:
Safety Protocols in Occupational Settings
- Training: Ensure that you and your team are well-trained in handling DEF. Understand the risks associated with exposure, particularly to the eyes.
- Emergency Procedures: Familiarize yourself with the emergency procedures in case of exposure, especially eye contact. This should include immediate washing and seeking medical attention.
- Regular Safety Audits: Conduct regular audits to ensure that all safety protocols are being followed in your workplace.
Recommendations for Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Protection: Always wear safety goggles when handling. Goggles should have a seal to prevent liquid from entering from any direction.
- Protective Clothing: Wear long-sleeved shirts and long pants or overalls. If splashing is possible, use waterproof aprons or similar protective clothing.
- Gloves: Use chemical-resistant gloves, such as nitrile gloves, to prevent skin contact.
Tips for Safe Handling and Storage of DEF Fluid at Home or in a Workshop
- Proper Storage: Store it in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight. DEF has a shelf life, typically about two years, but this can be reduced if stored improperly.
- Labeling: Clearly label all containers, and ensure they are sealed properly to avoid any accidental spills.
- No Cross-Contamination: Use dedicated equipment for DEF to prevent contamination. Never use the same funnels, jugs, or containers for other fluids.
- Spill Kit: Keep a spill kit nearby, including materials to contain and clean up spills, such as absorbent materials and a dedicated waste container.
- Disposal: Know the proper disposal methods for DEF and any contaminated materials. It is not just water and should not be treated as such.
Remember, the key to safely handling is awareness and proper preparation. By following these safety protocols and using the recommended PPE, you can significantly reduce the risk of fluid exposure. Stay vigilant, stay informed, and prioritize safety in all your interactions with DEF.
Read related article: How is DEF Different From Other Diesel Additives?
Legal and Workplace Safety Considerations
When you’re dealing with DEF in the workplace, it’s crucial to be aware of the legal and safety obligations. Understanding OSHA guidelines, employer responsibilities, and your rights as a worker can help ensure a safe working environment. Here’s a breakdown of key considerations:
OSHA Guidelines for DEF Fluid Handling
- Hazard Communication Standard (HCS): OSHA requires that all chemical hazards, including DEF, are communicated to workers. This means labels, safety data sheets (SDS), and proper training on handling it.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Employers must provide appropriate PPE, such as chemical-resistant gloves and safety goggles, to protect against exposure.
- Emergency Wash Stations: OSHA mandates that workplaces with chemicals like DEF should have accessible emergency eye wash stations, especially in areas where exposure risks are high.
Employer Responsibilities
- Training and Education: Employers are responsible for educating you about the hazards of DEF and the correct handling procedures. This includes training on using PPE and first aid measures in case of exposure.
- Providing Safety Equipment: It’s the employer’s duty to provide and maintain necessary safety equipment, including eye wash stations and appropriate PPE.
- Maintaining a Safe Workplace: Regular safety audits and risk assessments should be conducted to ensure a safe working environment.
Legal Recourse for Workers
- Worker’s Compensation: If you suffer an eye injury due to exposure at work, you’re typically entitled to worker’s compensation. This can cover medical expenses, lost wages, and rehabilitation costs.
- Reporting Non-Compliance: If your employer fails to comply with OSHA standards, you have the right to report these violations. OSHA protects you from retaliation for reporting unsafe working conditions.
- Seek Legal Advice: In cases of severe injury or if you feel your rights have been violated, consulting with a lawyer experienced in occupational safety and workers’ compensation can be a critical step.
As a worker handling DEF, it’s important for you to be proactive about your safety. Familiarize yourself with the safety protocols, make use of the provided protective equipment, and don’t hesitate to voice concerns about workplace safety practices. Remember, understanding your rights and responsibilities is not just about compliance; it’s about ensuring a safe and healthy working environment for you and your colleagues.
Conclusion
In wrapping up our discussion of the risks associated with Diesel Exhaust Fluid exposure to the eyes, it’s clear that this common substance in diesel engine maintenance is not as innocuous as one might think. The journey through the chemical composition of DEF, its interaction with the tissue, and the potential for both short-term discomfort and long-term damage underscores a crucial message: vigilance and proper safety measures are indispensable.
Remember, the combination of 32.5% urea and 67.5% deionized water in DEF, while effective in reducing vehicle emissions, poses a significant risk to eye health. From the immediate irritation, redness, and burning sensation to the more severe risks of corneal damage and chronic eye conditions, the dangers are real and should not be underestimated.
As we’ve discussed, the key to mitigating these risks lies in education, proper handling, and swift response to exposure. Whether it’s through adhering to OSHA guidelines in the workplace, equipping yourself with the right personal protective equipment, or understanding the correct first aid measures, each step is vital in protecting your eyes.
Moreover, the role of employers in ensuring a safe work environment and the legal recourses available to workers highlight the broader context in which these safety practices operate. It’s not just about individual actions; it’s about creating a culture of safety and responsibility.
In closing, I urge you to take these insights seriously. Whether you’re a professional working with the fluid regularly or an individual handling it occasionally, the responsibility to protect your eyes is paramount. By staying informed, prepared, and proactive, you can significantly reduce the risk of harm and ensure that your vision, one of your most precious senses, is safeguarded against the potential dangers of DEF. Stay safe, stay aware, and prioritize your health always.
